Azure Load Balancer
Azure Load Balancer is a Layer 4 (TCP/UDP) service that distributes incoming or outbound network traffic across multiple VMs or instances to improve availability and performance. It provides high availability by automatically directing traffic only to healthy backend resources using health probes.
Load Balancer
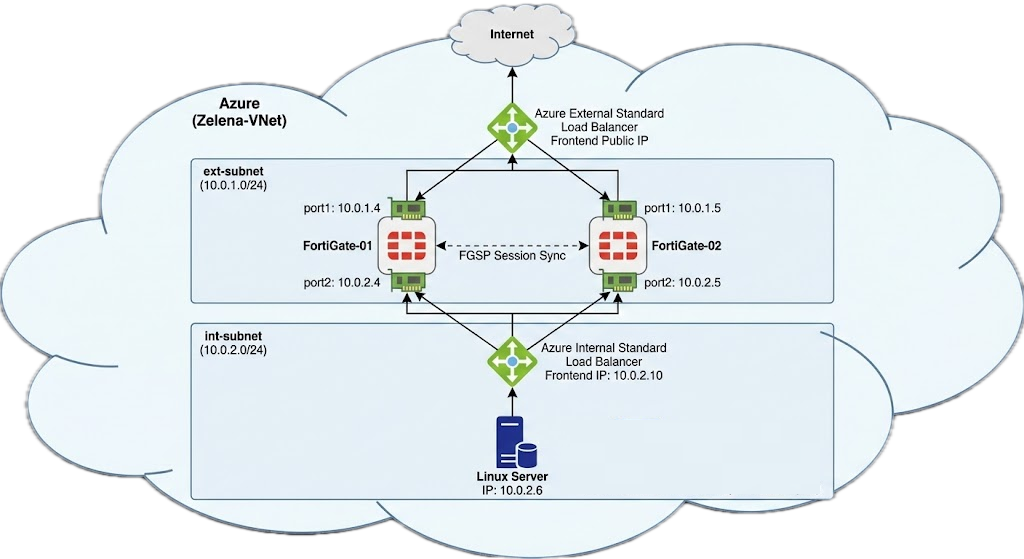
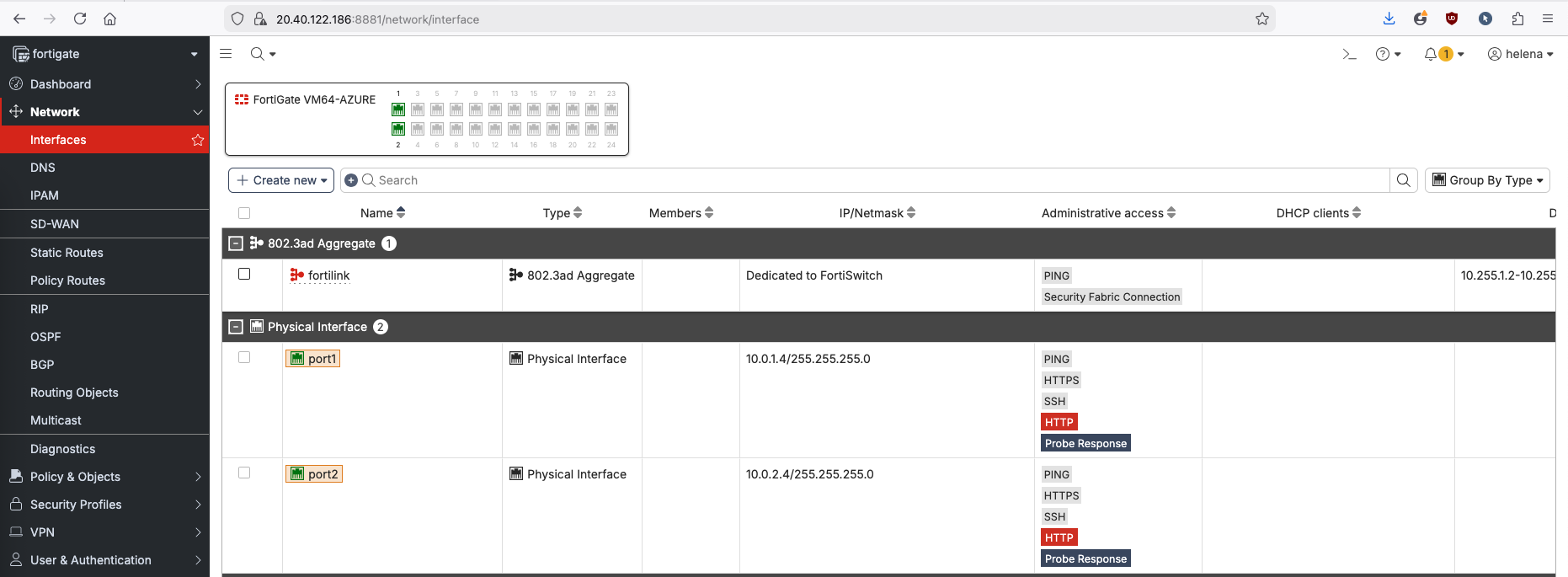
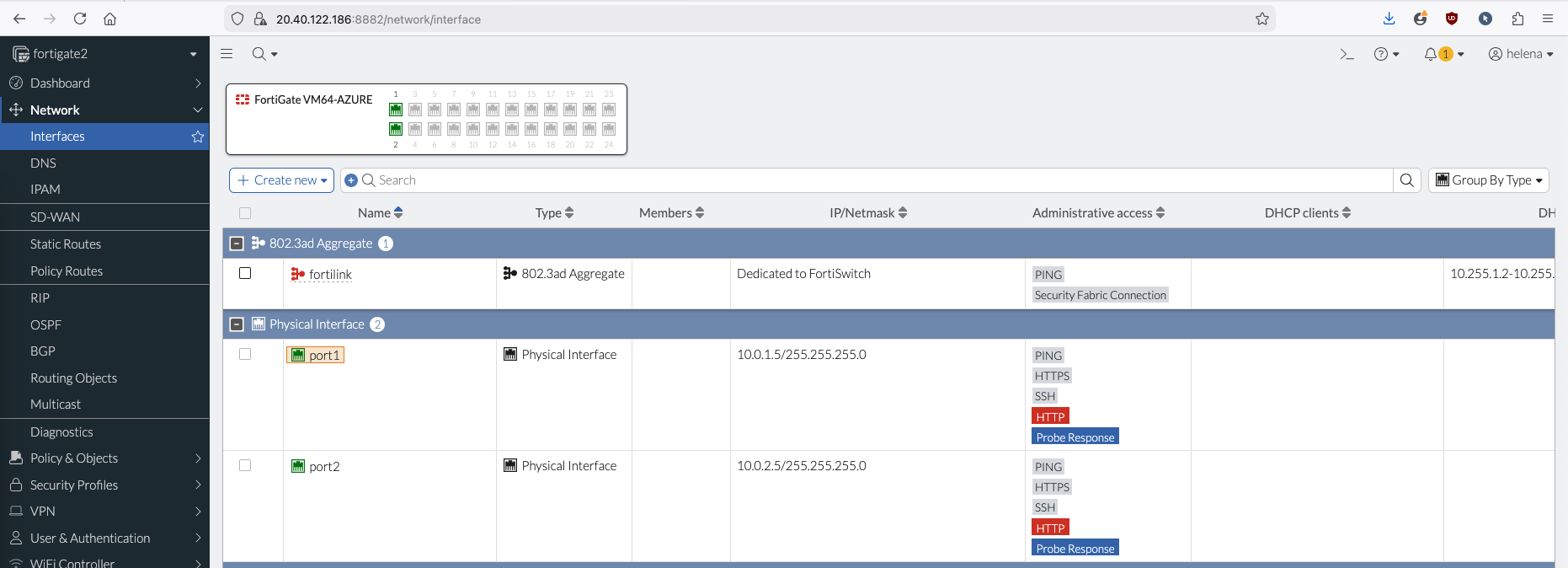
Here we have our 2 standalone foritgates setup with each having ext and int interfaces
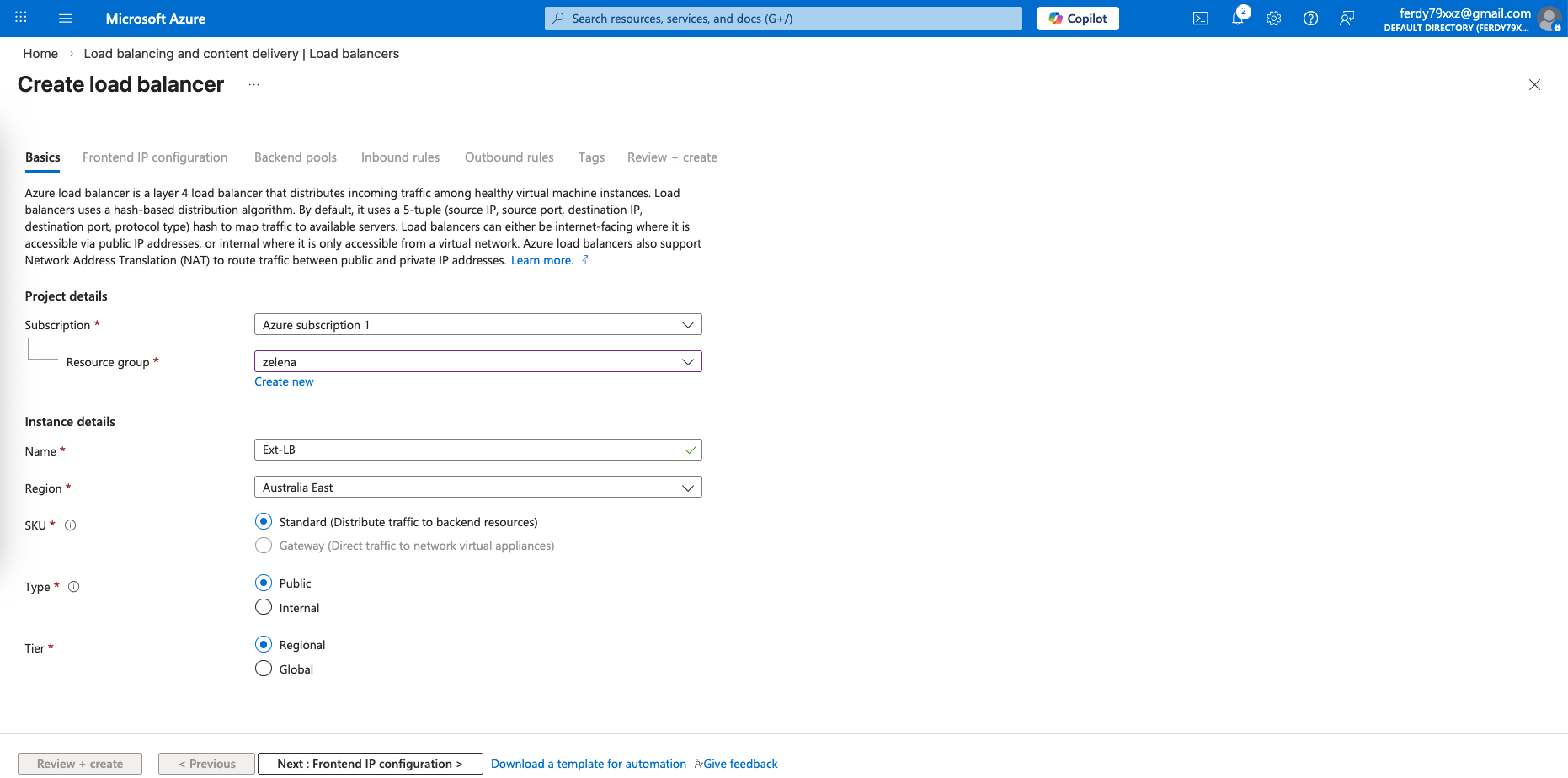
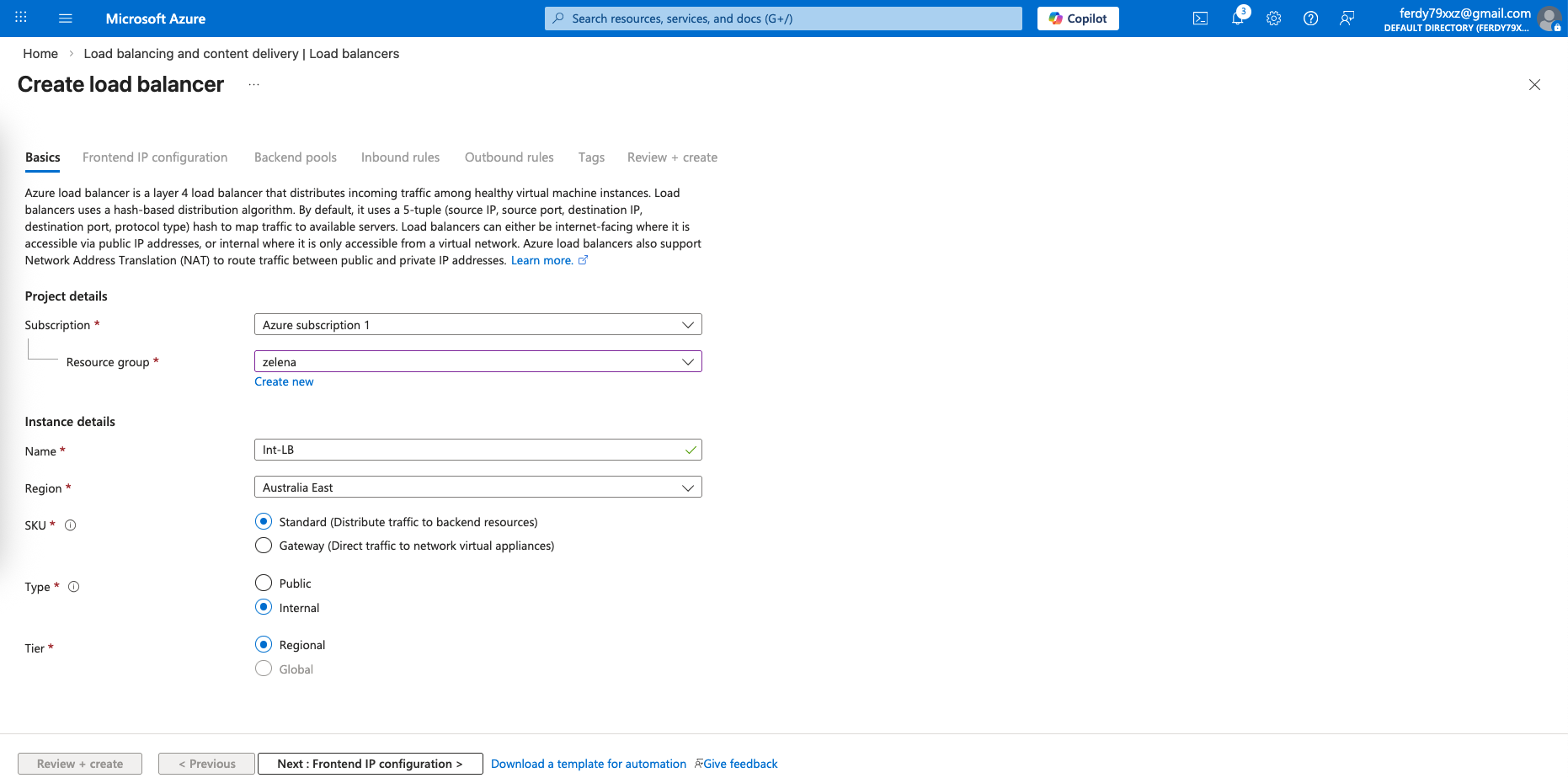
Next we go to Load Balancer page and create a Standard Load Balancer
External LB
First we create the External LB with type Public
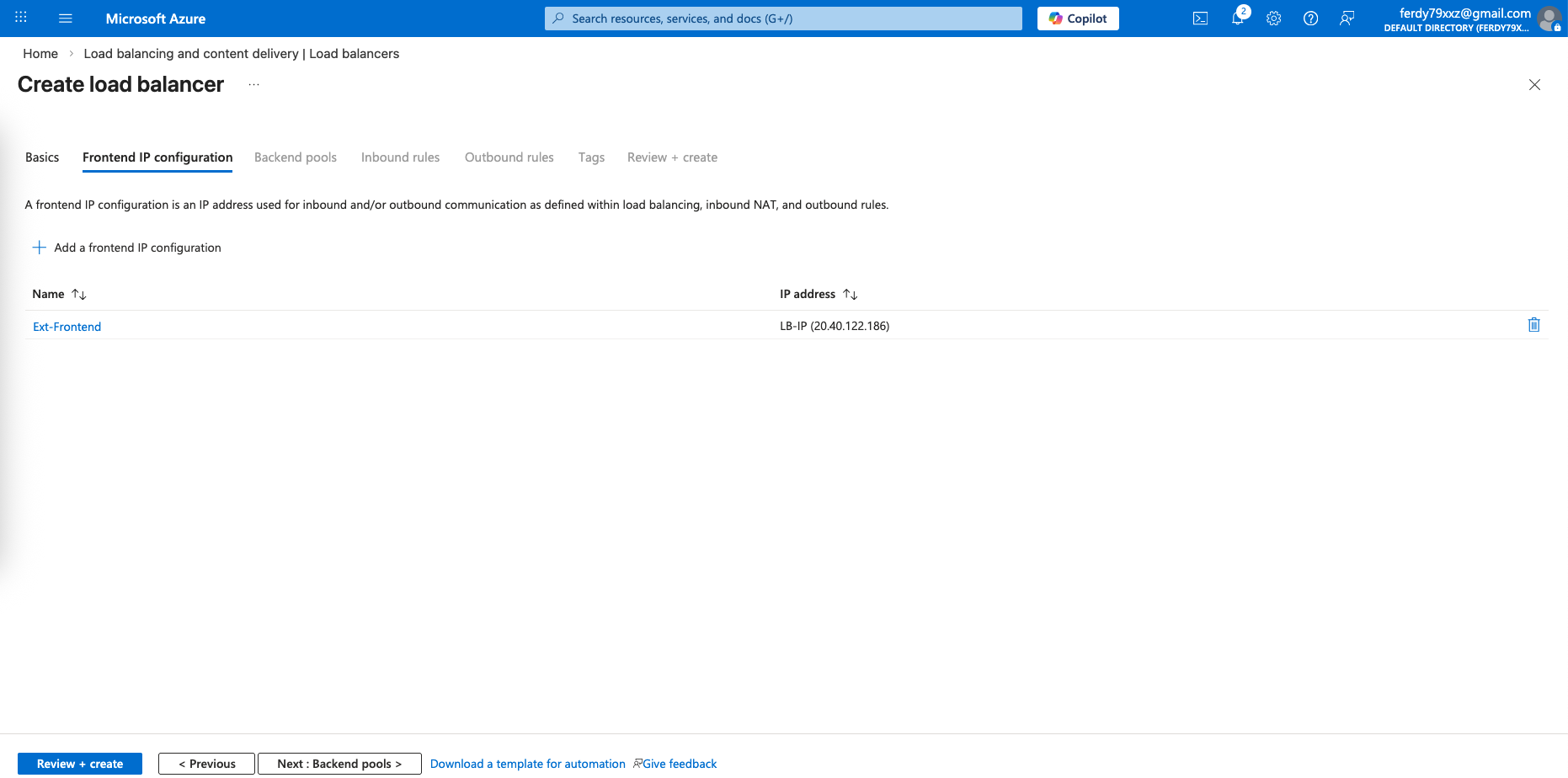
Then we give it a Public IP for the Frontend configuration
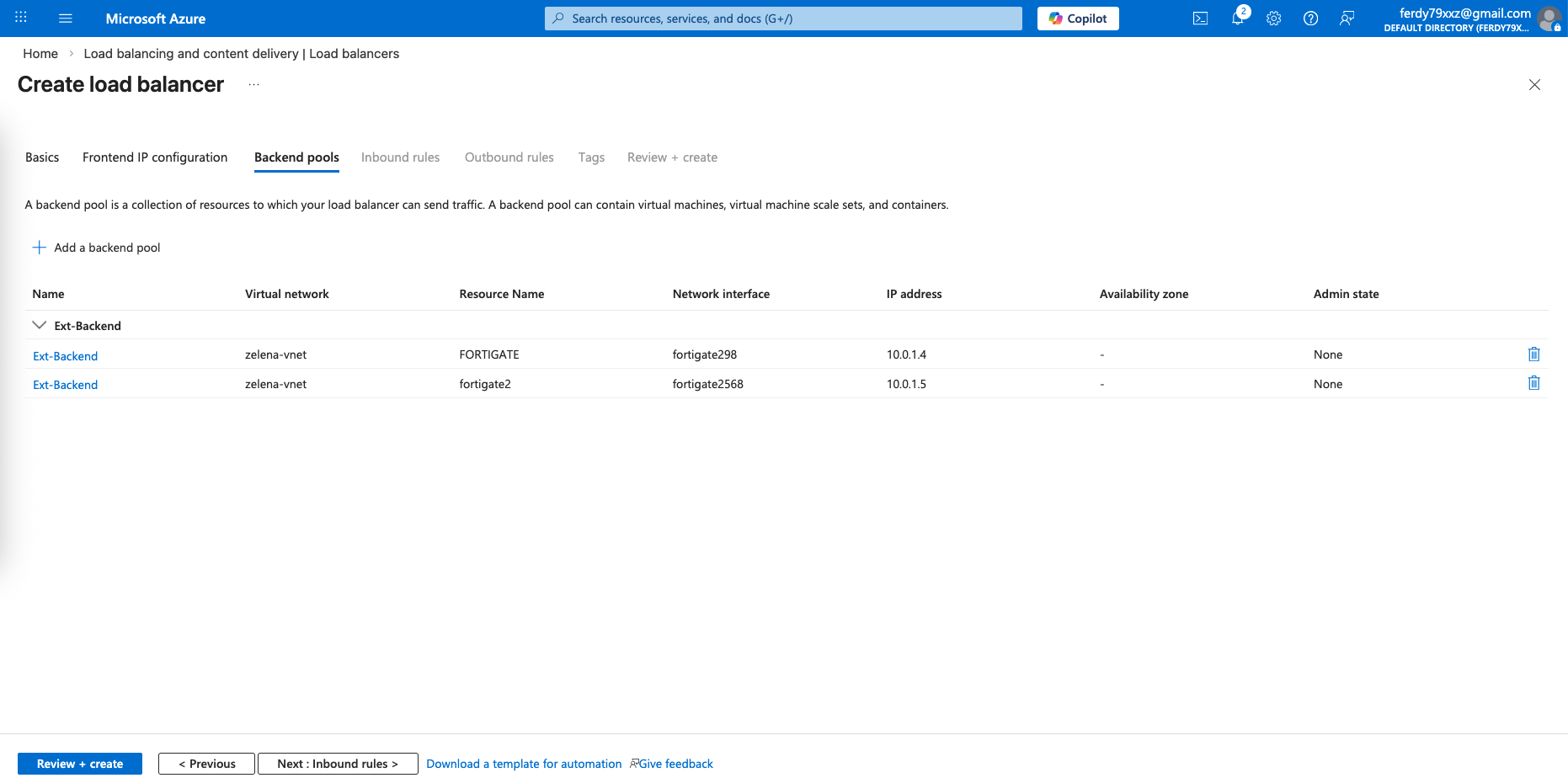
On the Backend Pools, we select both our Fortigate’s external interfaces
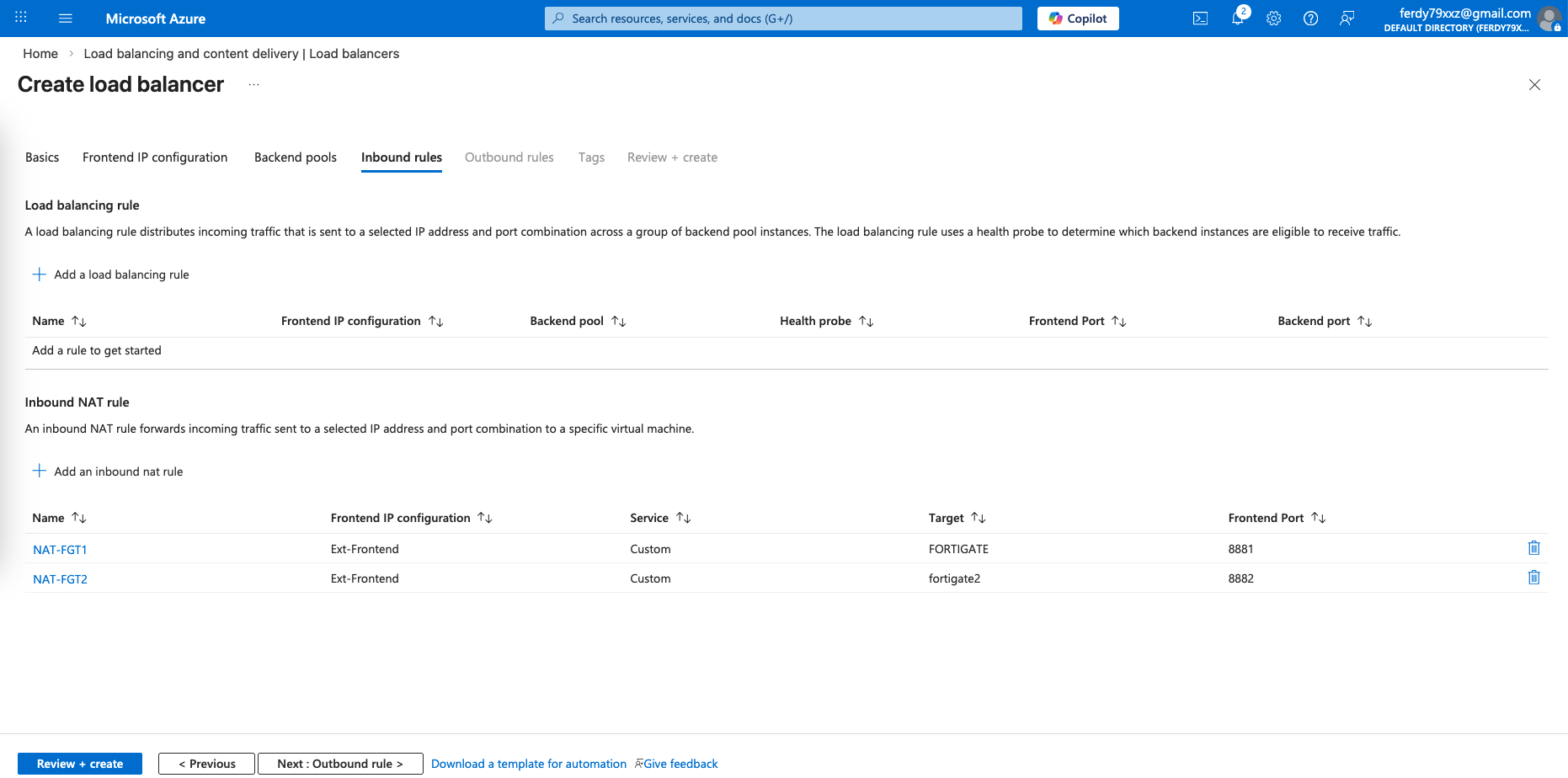
This is optional and for management only, because we want to be able to manage each of our FGTs using a single Public IP, we will use Inbound NAT to forward port 8881 and 8882 to each fortigate respectively
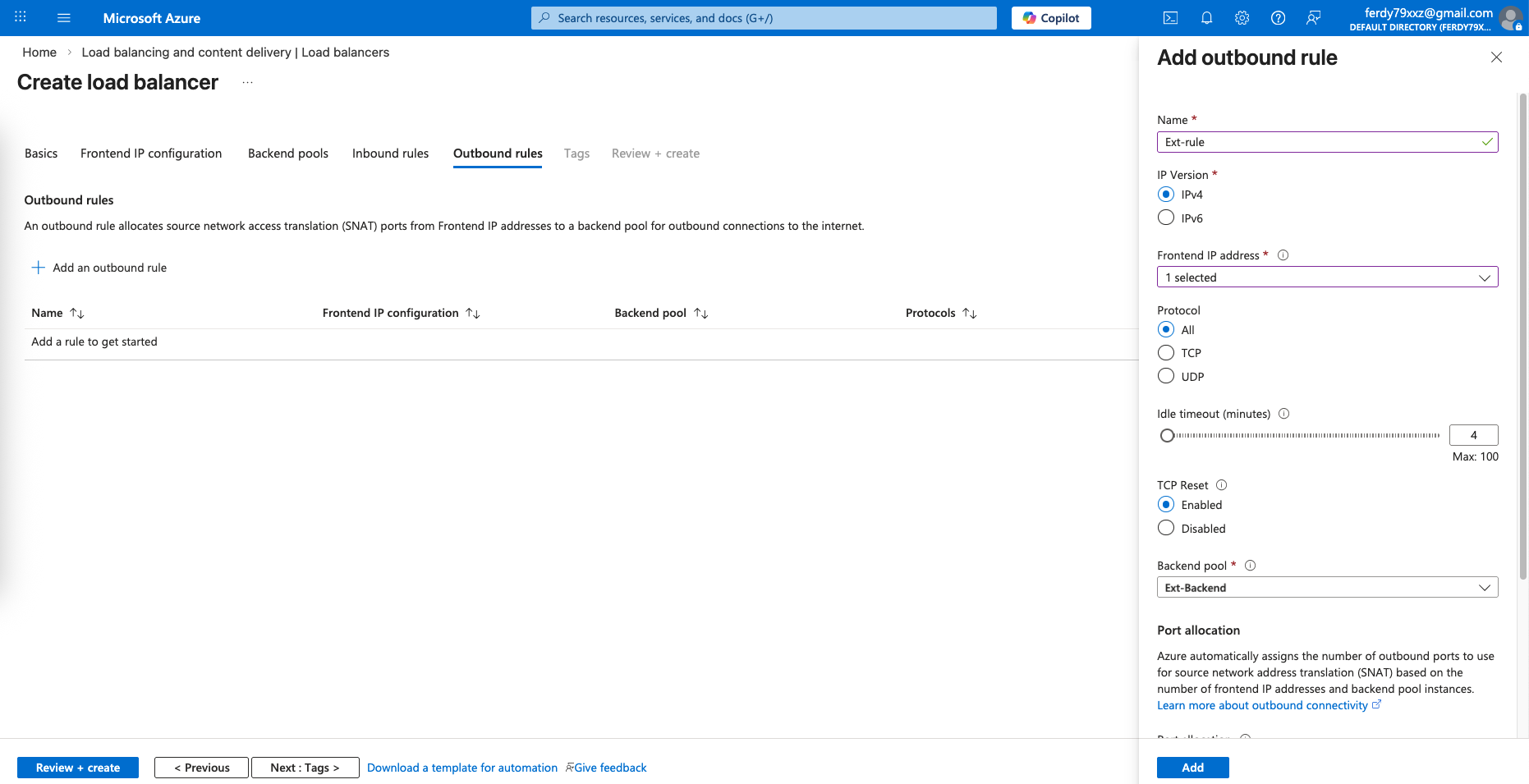
Then we’d also need an Outbound rule to allow traffic going out to the internet
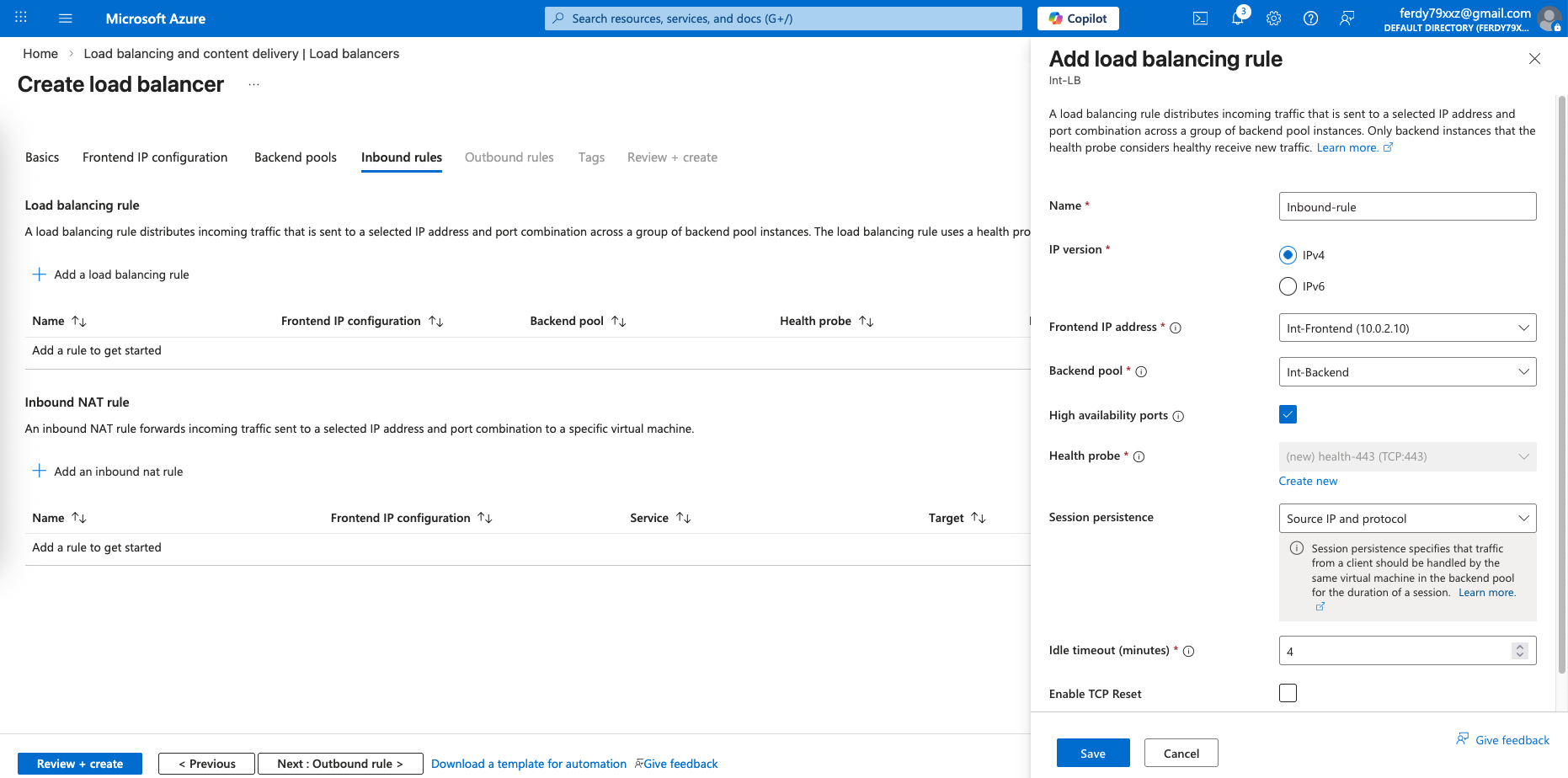
Internal LB
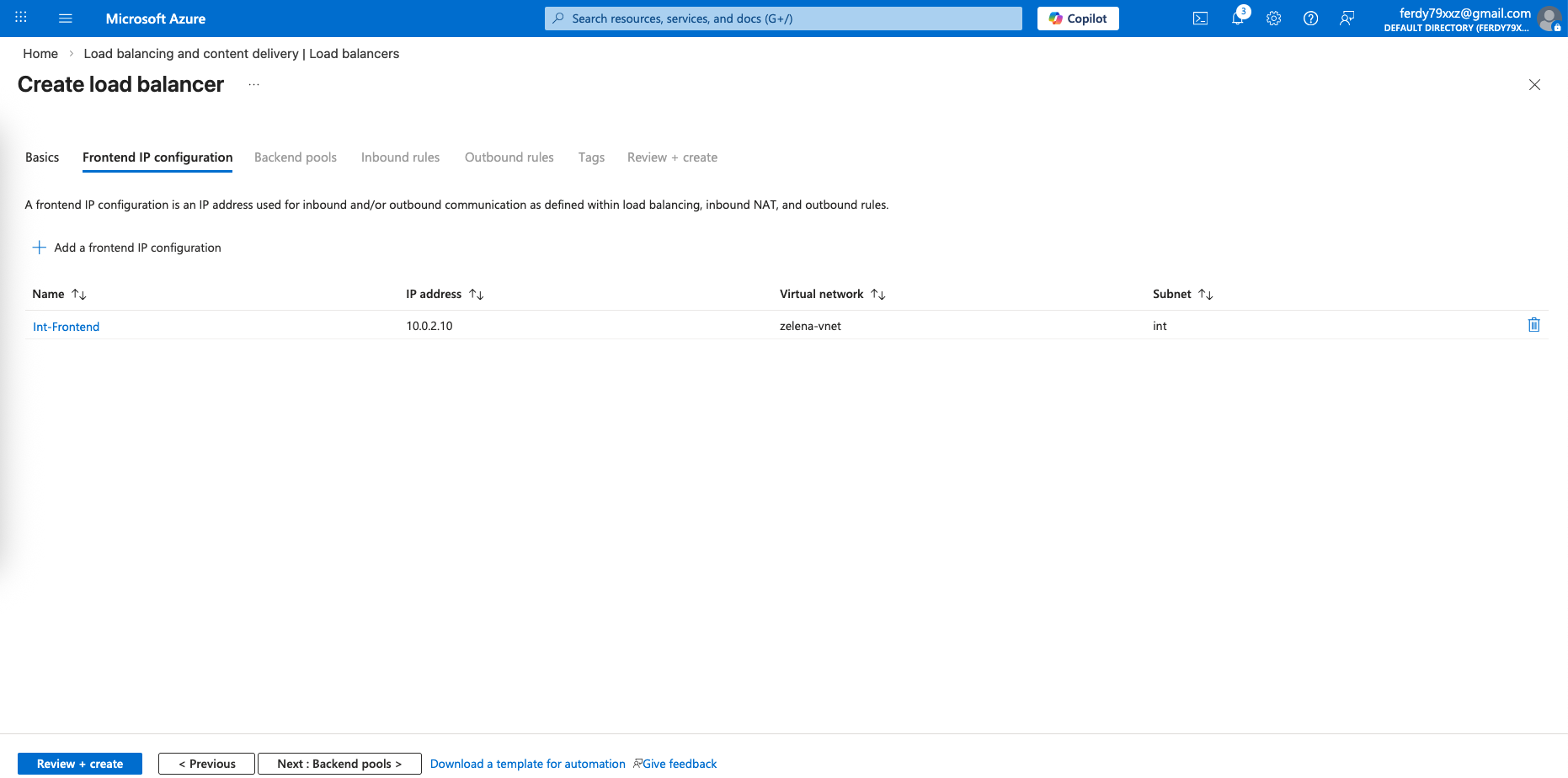
After that we configure the LB for the Internal side
We configure an LB IP Address on the same subnet as our fortigates’ internal interfaces
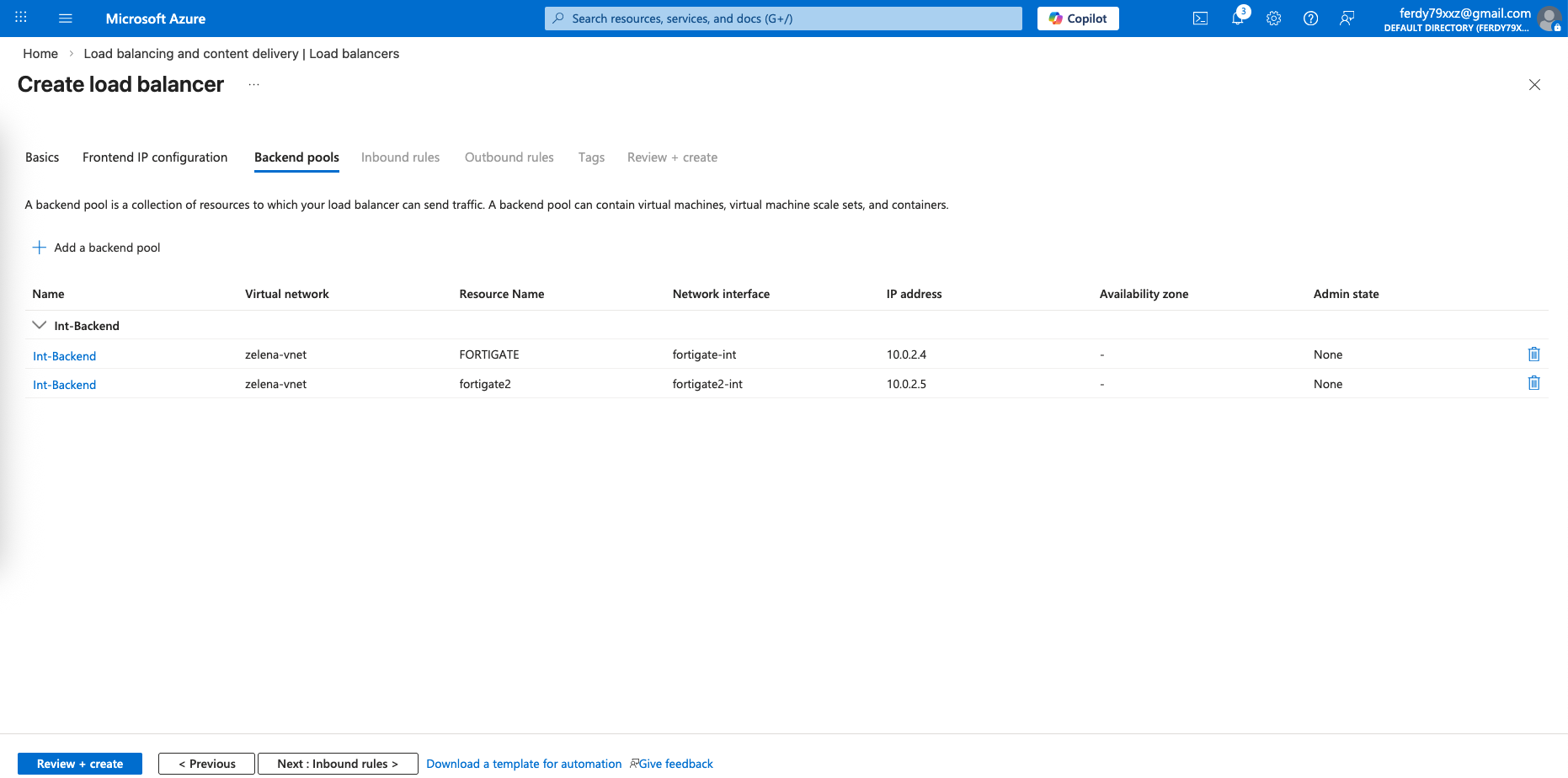
And we select both our fortigates’ internal interfaces for our Backend Pools
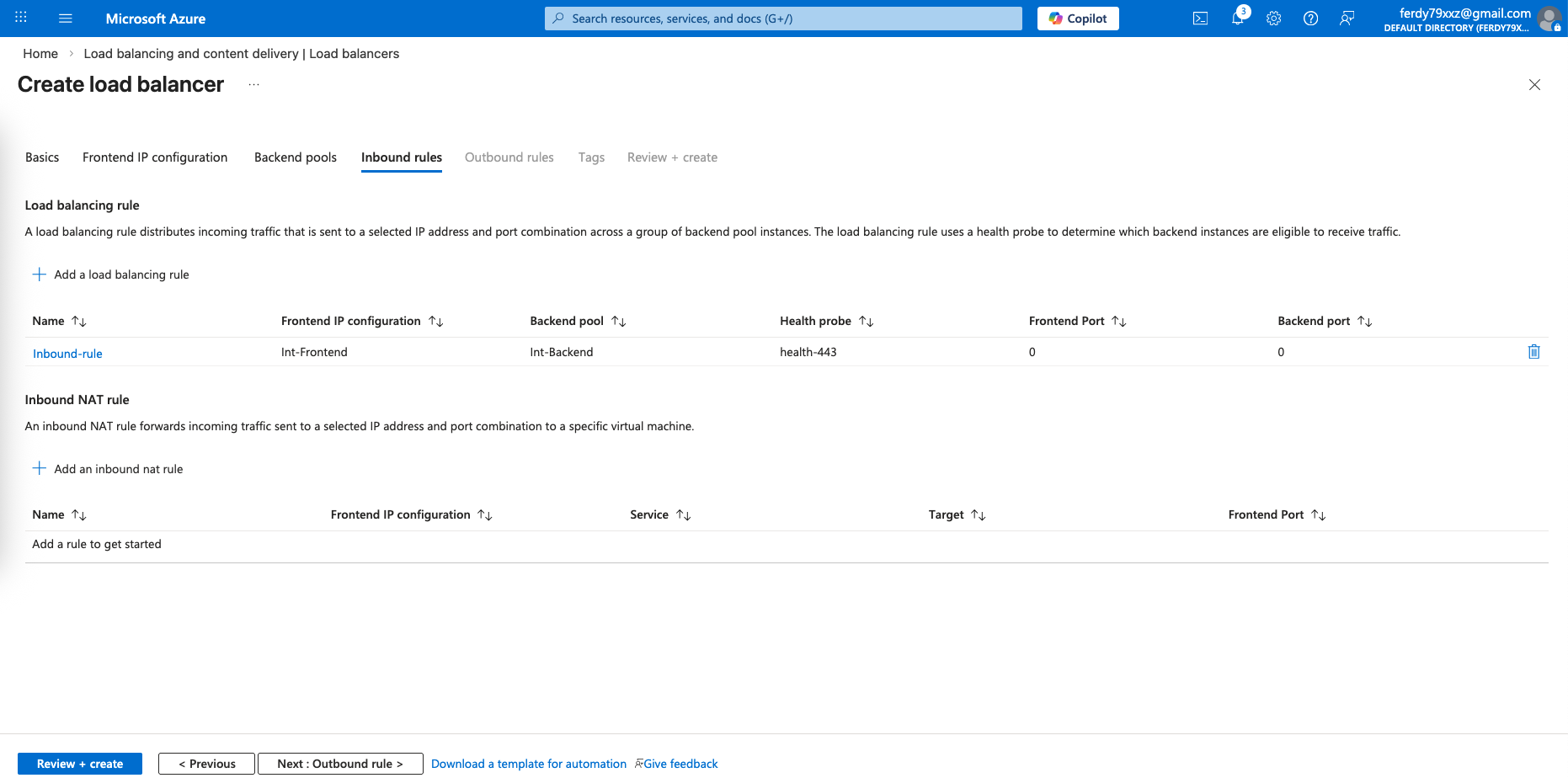
After that we will need an Inbound rule to allow traffic coming in from our clients, we also configure Health Probe to check fortigates’ health status
And that should round up our LB configurations
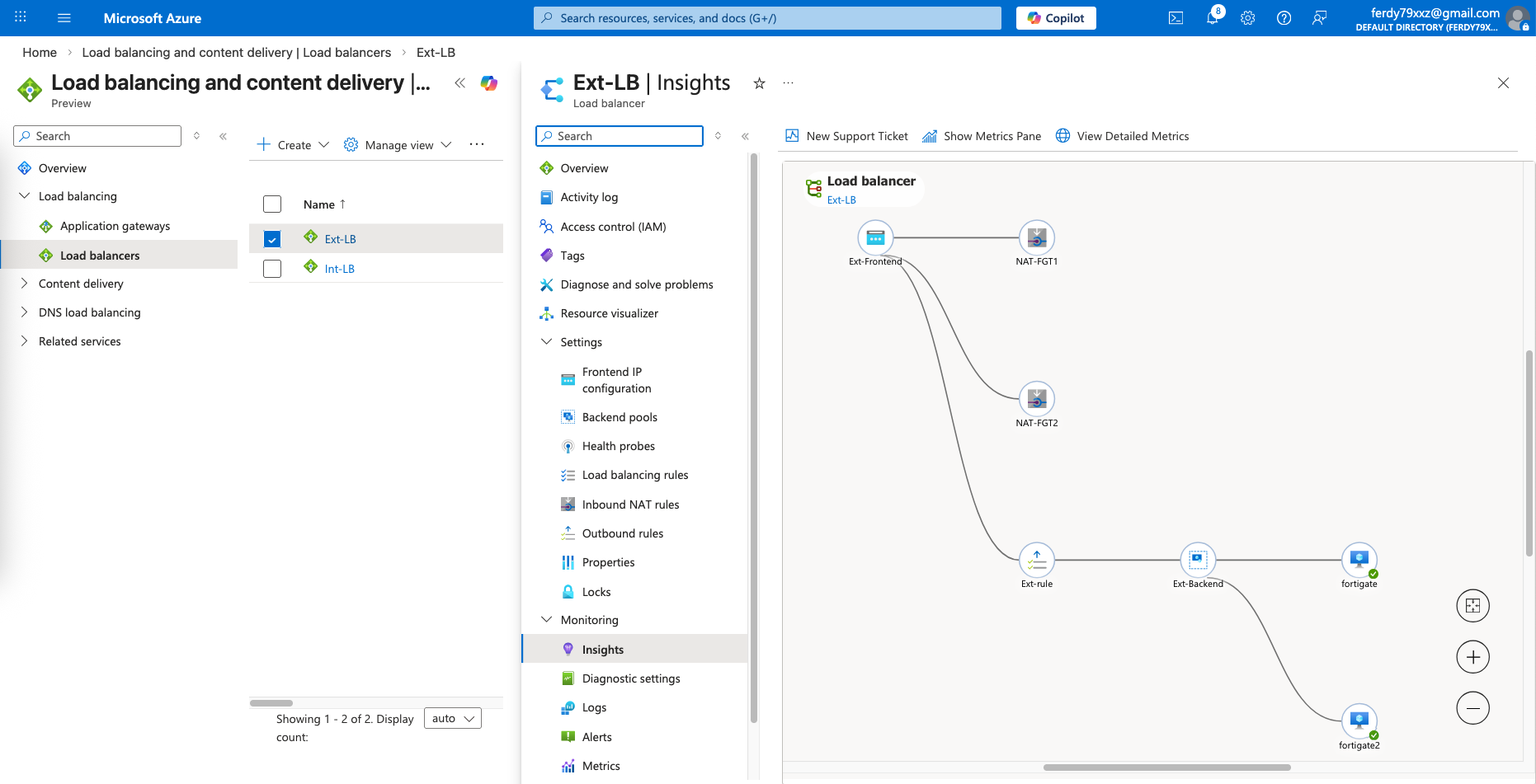
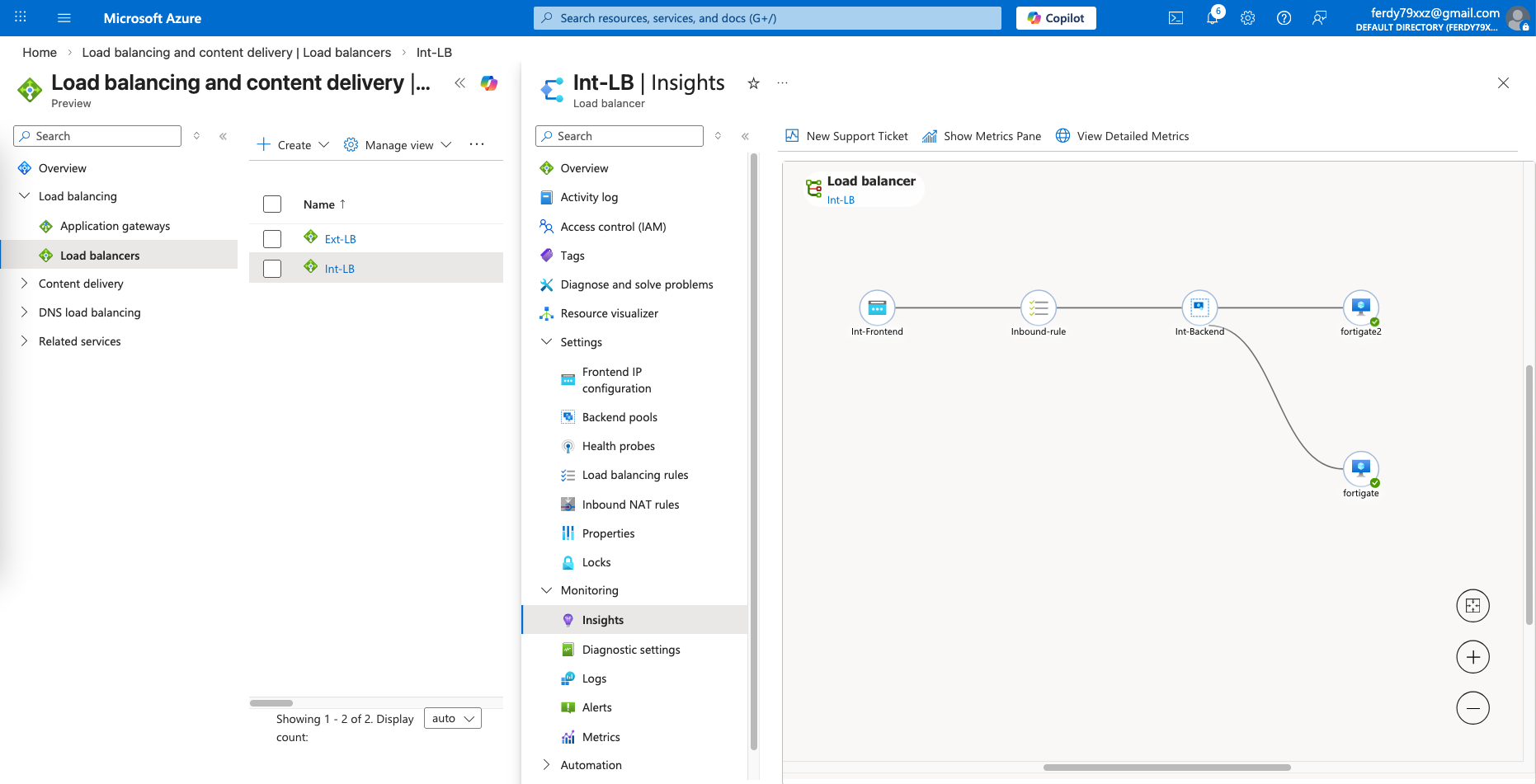
Load Balancer Insights
Here we can see the Insights for each LB topology, showing the members of the LB and their statuses
Ext
Int
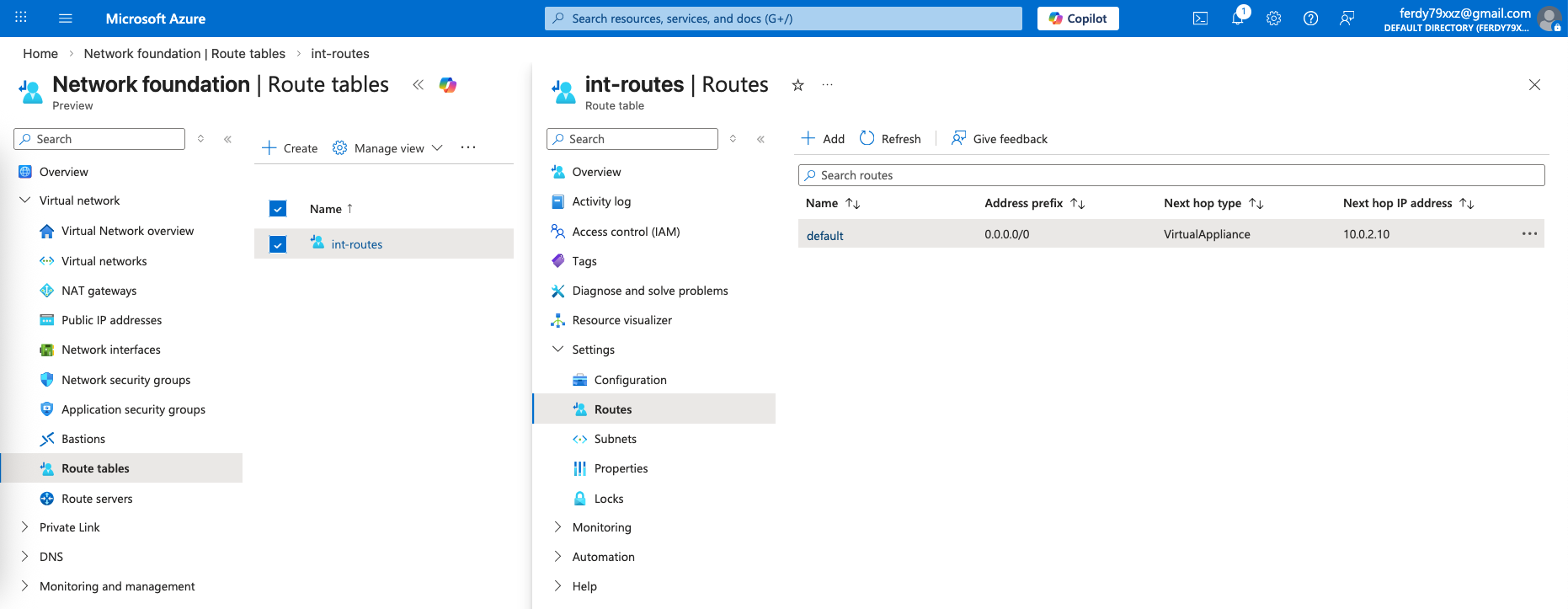
Routing
Lastly we need to route our clients’ traffic to go out using our Internal LB IP Address
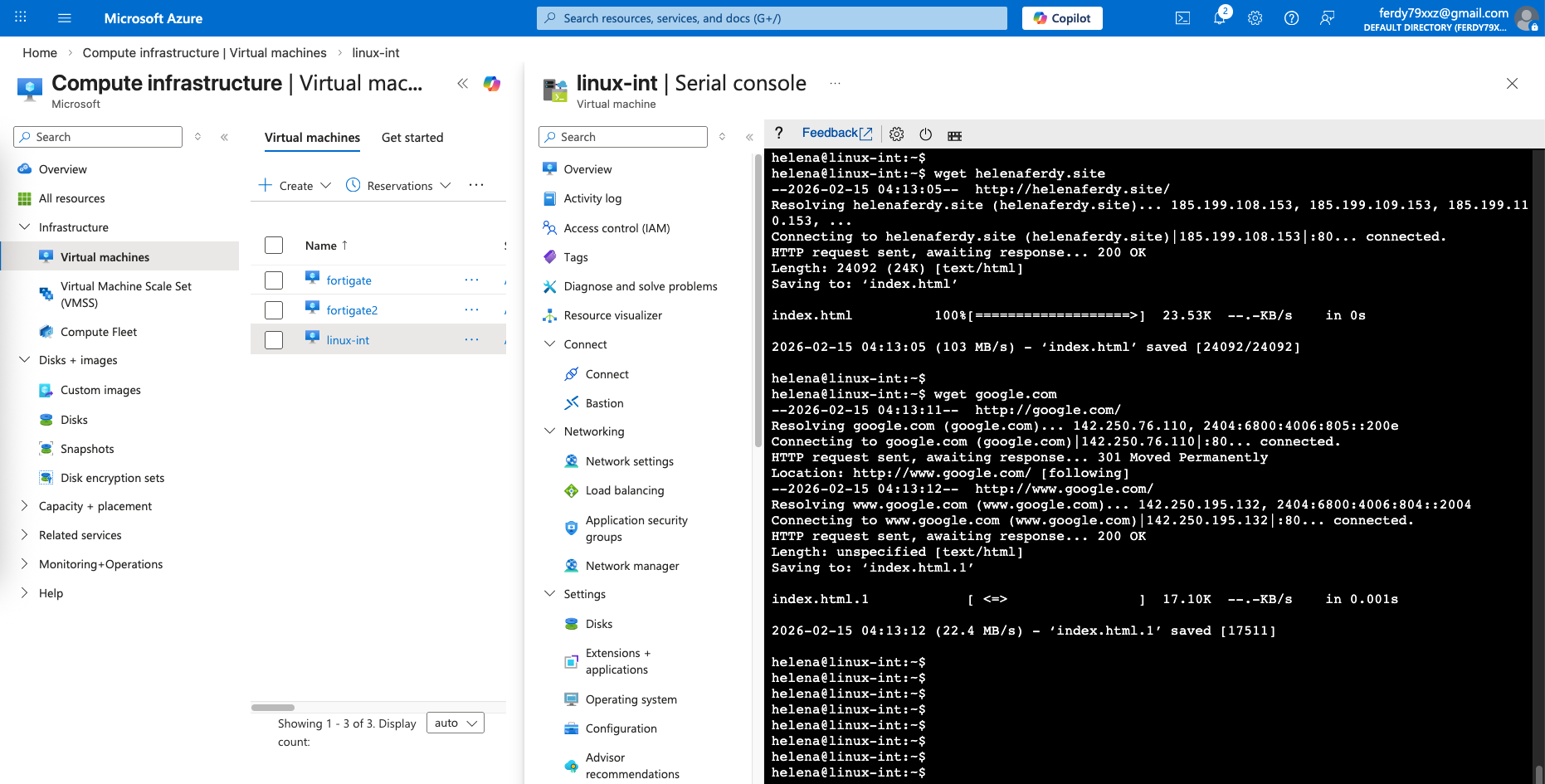
Testing
Now we can test it from a linux server inside the Internal Subnet, verifying that this client can access internet just fine
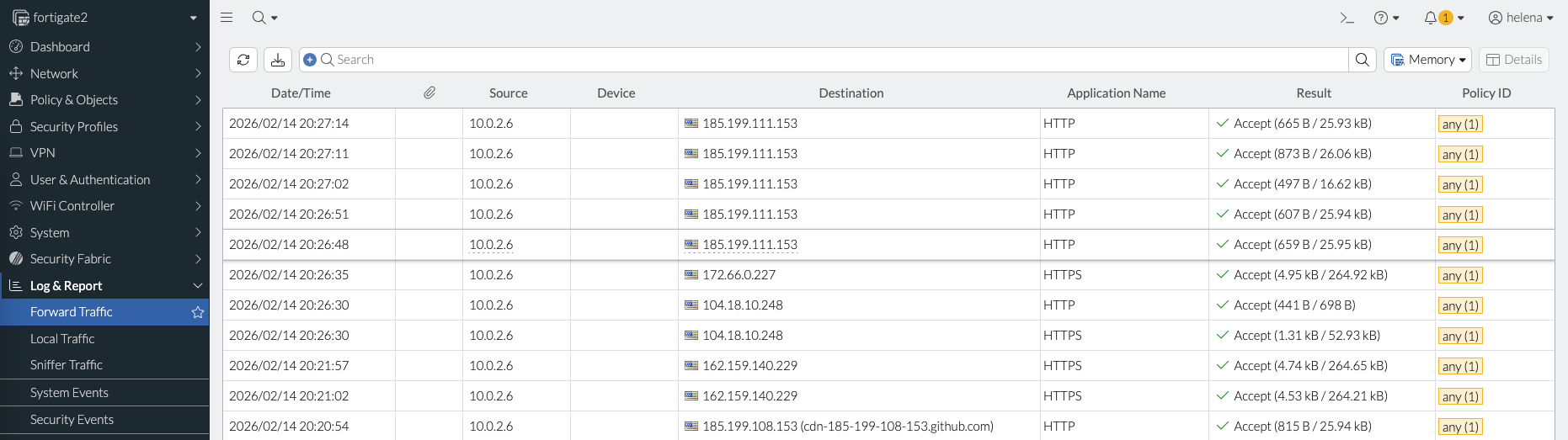
The traffic from the client is load balanced to 2 fortigate instances
Since we also configured the Inbound NAT, we can access each foertigate using port 8881 or 8882